Structure of a gene and its control elements
Authors
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37980/im.journal.ggcl.en.20252684Keywords:
genes, clinical applications, literature reviewAbstract
Knowledge of the structure, regulation, and function of genes is a fundamental pillar of molecular biology and modern medicine. Genes are DNA sequences that contain the information necessary to produce functional proteins or RNA, and are not only made up of coding regions (exons), but also introns and regulatory elements such as promoters, enhancers, and silencers. Mutations in any of these regions can alter normal cellular function and lead to various diseases. The regulation of gene expression ensures that not all genes are activated at the same time, but rather in a controlled manner depending on the cell type, stage of development, or environmental conditions. This control is mediated by transcription factors, epigenetic modifications such as DNA methylation, and the action of non-coding RNAs, mechanisms that allow multiple specialized cell types to be generated from the same DNA sequence. The function of genes is reflected in the products they encode, whether proteins or RNA, which participate in vital processes such as metabolism, cell signaling, or DNA repair. Genetic variants can cause loss of function, as in the case of cystic fibrosis due to mutations in the CFTR gene, or gain of function, as occurs in certain oncogenes involved in cancer.
INTRODUCTION
A gene is the fundamental unit of heredity and constitutes a defined segment of DNA that contains the necessary information for the synthesis of functional products, whether they are proteins or non-coding RNA molecules [1]. These elements play an essential role in the transmission of hereditary characteristics, in the regulation of biological processes, and in cellular differentiation, making them key pieces for both molecular biology and modern medicine [2].
The structure of a gene is not limited to the sequences that encode proteins (exons), but includes multiple regulatory regions that determine when, where, and in what quantity a gene will be expressed. Among these are the promoter, which allows the initiation of transcription; introns, non-coding sequences removed in the RNA maturation process; and untranslated regions (UTR), which regulate the stability and translation of mRNA [3]. Likewise, proximal and distal control elements, such as TATA boxes, CAAT boxes, enhancers, and silencers, precisely modulate gene activity [1,4].
Together, this structural and regulatory organization ensures the correct expression of genes, allowing cells to respond to internal and external stimuli, maintain their identity, and coordinate essential functions for the development and homeostasis of living organisms [5].
METHODOLOGY
The present research was carried out through a bibliographic review. For this purpose, different genetics compendiums were consulted, including books in both physical and digital formats. Additionally, updated scientific articles were reviewed, selecting those that provided relevant and well-founded information for the development of the report. The most pertinent data were extracted, analyzed, and synthesized to construct clear and coherent content aimed at preparing educational material for medical and basic science students.
What is a gene?
A gene is the physical and functional unit that occupies a specific position (locus) in the genome. It corresponds to a nucleotide sequence that encodes one or more functional products (ncRNA and polypeptides) and whose expression is controlled by regulatory elements [6].
Structural parts of the gene (eukaryotes)
Eukaryotic genes have various structural regions that control their expression (See Image 1):
• Promoter: It is the DNA region where RNA polymerase and other transcription factors bind to initiate the transcription process.
• Exons: These are DNA sequences that encode the information for protein synthesis. After transcription, exons are "spliced" (joined) to form mature mRNA.
• Introns: These are non-coding DNA sequences interspersed between exons. They are transcribed into mRNA but are then removed from the immature mRNA (pre-mRNA) through "splicing" before the protein is synthesized. They are not translated into amino acids.
• Transcription Start Site (TSS): It is the first DNA base that is transcribed into RNA. It is located within or just after the promoter region.
• Translation Start Site (Start Codon): It is the three-base sequence (usually AUG) in the mRNA that signals the beginning of protein synthesis. It corresponds to a specific triplet in the DNA.
• Translation Termination Site (Stop Codon): It is the three-base sequence that signals the end of protein synthesis.
• Untranslated Regions (UTRs): These are RNA sequences present in mature mRNA but not translated into protein. 5' UTR: Located at the beginning of the mRNA, before the start codon. It influences mRNA stability and translation efficiency. 3' UTR: Located at the end of the mRNA, after the stop codon.
• Terminator Sequence: It is a sequence in the DNA that signals the end of the transcription process. In eukaryotes, it often includes a sequence that, in the mRNA, indicates the site where a poly-A tail (many adenines) is added at the 3' end [7,8].
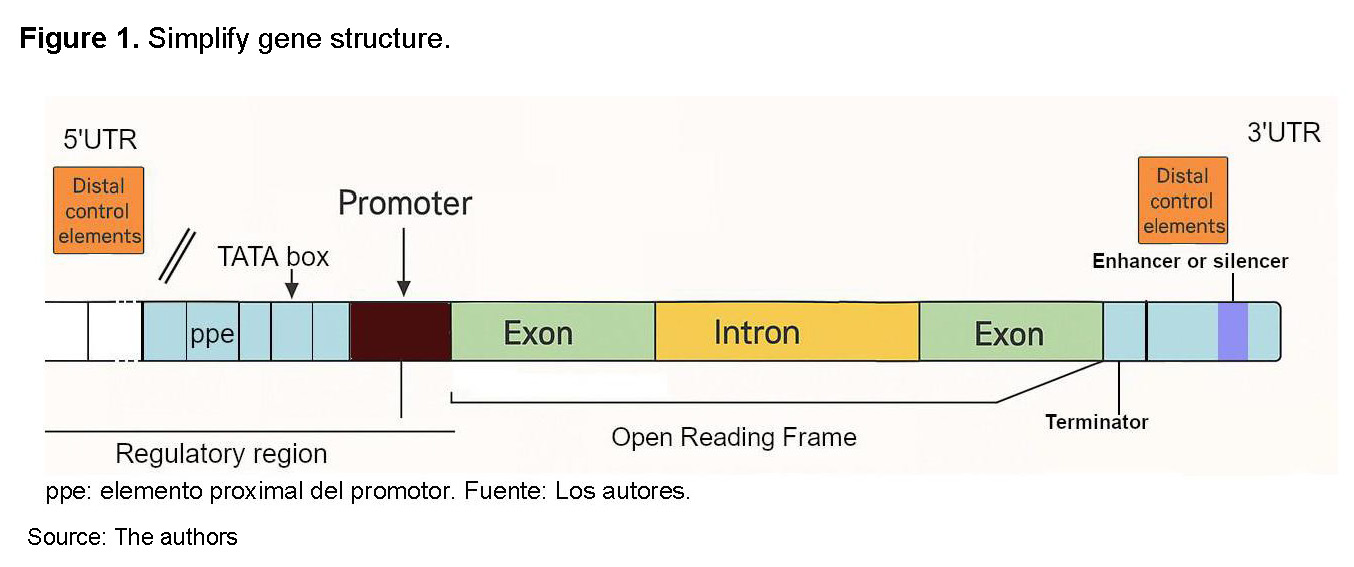
GENE CONTROL ELEMENTS
Proximal control elements
Proximal control elements are regulatory DNA sequences located near the transcription start of a gene. Their main purpose is to control transcription, that is, the process of "reading" the gene's information to create proteins. These elements are located in a region close to the transcription start site, generally within a few hundred base pairs upstream, and function as anchoring points for specialized proteins that modulate gene expression [9].
Within this region, there are two types of crucial elements. The first is the basal promoter, which is the DNA sequence closest to the transcription start site and is indispensable for the process to occur. It is here that the RNA polymerase enzyme binds along with general transcription factors to form the pre-initiation complex. A key example within the basal promoter is the TATA Box, a sequence that helps position the transcription machinery correctly. The second type is the proximal regulatory elements, located just before the basal promoter. These sequences are recognized by specific transcription factors that act as switches, increasing (activators) or decreasing (repressors) the activity of the basal promoter to fine-tune the transcription rate. Examples of these elements include the CAAT Box and the GC Box [9].
In essence, proximal control elements function as binding platforms. By modulating the transcription rate, these elements are fundamental for the specificity of gene expression. This ensures that genes are turned on or off at the right time and place, allowing a cell to specialize and respond to signals [9].
Distal control elements
Distal control elements of a gene are regulatory DNA sequences located far from the transcription start site of the gene they affect, unlike proximal elements that are nearby [10,11].
The two types are:
• Enhancers: These are DNA sequences that increase the transcription rate of a gene and act by binding transcription factors. These factors, in turn, interact with the basal transcription complex at the gene's promoter, often through DNA looping, bringing distal regions closer to proximal ones. The action of enhancers is often tissue-specific or development stage-specific, allowing fine regulation of gene expression in different cellular contexts [11,12].
• Silencers: These are DNA sequences that, on the contrary, decrease or suppress the transcription rate of a gene. They can also be found at considerable distances from the target gene. Like enhancers, silencers act by binding repressor transcription factors in various ways, such as blocking the binding of activator transcription factors, recruiting proteins that modify chromatin to make it more compact, or directly interfering with the transcription machinery [11,13].
Epigenetic Regulation and Chromatin
Chromatin and its Function
Chromatin is the structure composed of DNA and proteins that packages genetic material in the cell nucleus. Its main function is to compact DNA so that it can fit in the limited space of the nucleus [1]. This structure is not fixed but can alternate between a condensed state (heterochromatin) and a more relaxed state (euchromatin). This malleability is crucial for gene regulation, as genes can only be read by the cellular machinery when chromatin is in its most relaxed state [14,15].
Epigenetic Regulation
Epigenetic regulation refers to modifications that affect gene expression without altering the DNA sequence. The term "epi" (meaning "above") highlights that these mechanisms act above the genetic code [16]. These changes are essential for cellular differentiation, are influenced by environmental factors such as stress or diet, and, unlike mutations, are reversible and can be inherited by daughter cells and, in some cases, by offspring [17,18].
Epigenetic mechanisms
The main epigenetic mechanisms work through chromatin modification [19]. DNA methylation, which involves adding methyl groups to cytosine bases, usually silences genes by preventing transcription (See Figure 2) [20]. Similarly, histone modifications, such as acetylation and methylation, alter chromatin compaction. Acetylation, for example, tends to relax the structure and facilitate transcription, while methylation can have activating or repressive effects, depending on the specific histone modified [21].
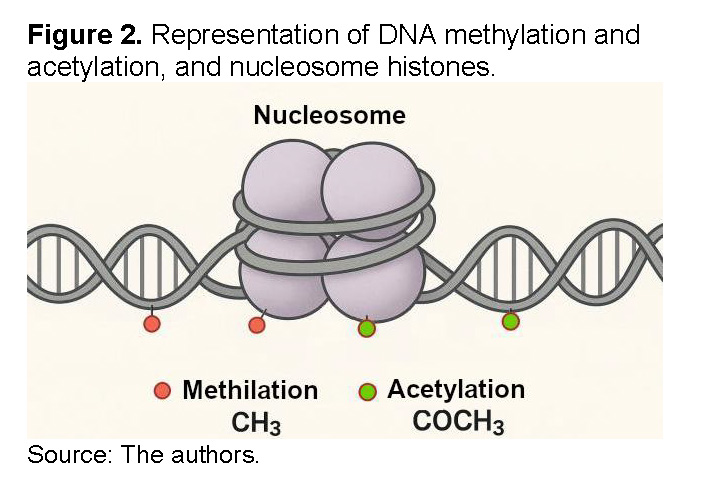
Nucleosomes are a key piece in this process because their structure and the chemical modifications they undergo determine the degree of chromatin compaction, which is the material chromosomes are made of. When chromatin is highly compacted, it is called heterochromatin, and the DNA is inaccessible, silencing the genes. Conversely, when chromatin is relaxed, known as euchromatin, the DNA is exposed, and genes can be transcribed and expressed.
CONCLUSION
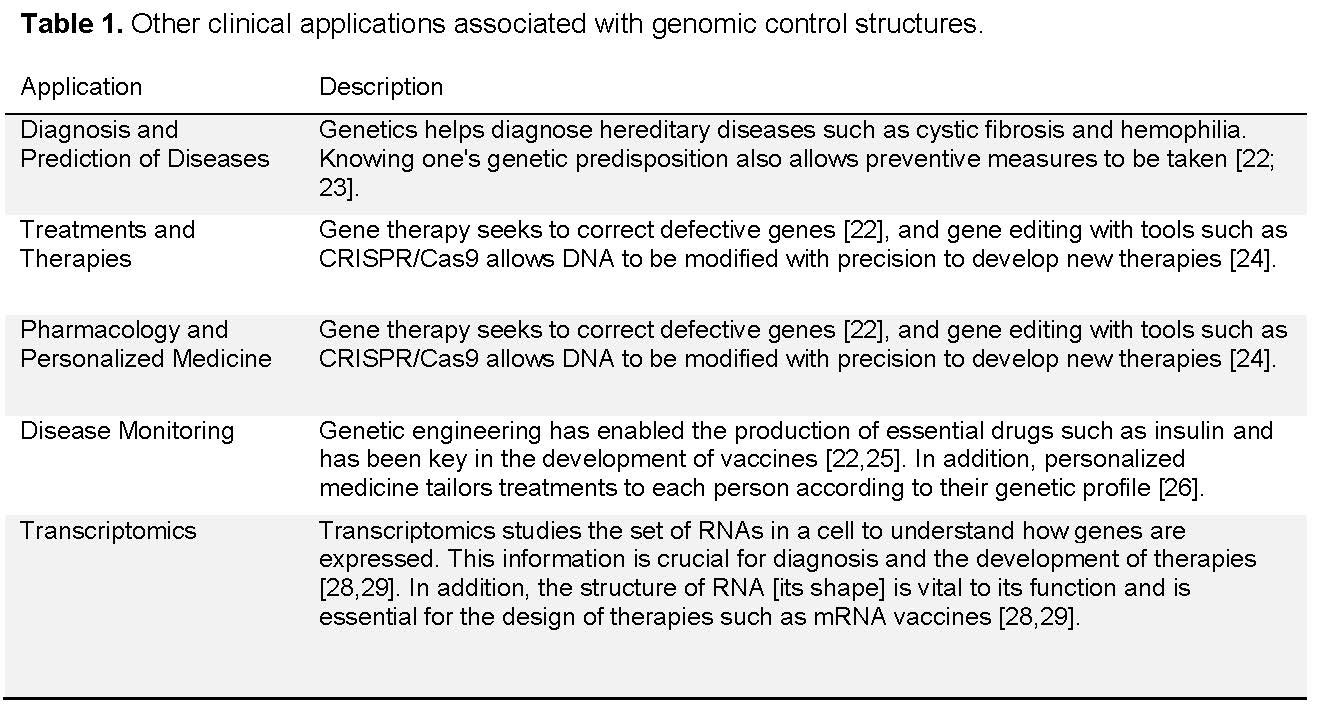
A gene is a functional unit of DNA that occupies a specific locus and has structures such as promoters, exons, introns, and UTR regions that determine its expression. These genes are regulated by proximal control elements (such as the TATA box) and distal elements (such as enhancers and silencers), which allow precise adjustment of their activity. Additionally, chromatin, in the form of heterochromatin or euchromatin, regulates access to DNA and is influenced by epigenetic mechanisms such as histone methylation and acetylation. These regulations are essential for development, cellular differentiation, and response to environmental stimuli. In medicine, the study of genes allows for the diagnosis of diseases, the design of personalized treatments, the application of gene therapies, and the monitoring of disease progression.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Jorge Mendez Rios for his support in the writing and critical review of this manuscript.
References
[1] Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Morgan D, Raff M, Roberts K, et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 6th ed. New York: Garland Science; [2014]
[2] Watson JD, Baker TA, Bell SP, Gann A, Levine M, Losick R. Molecular Biology of the Gene. 7th ed. San Francisco: Pearson; [2013]
[3] Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky SL, Matsudaira P, Baltimore D, Darnell J. Molecular Cell Biology. 9th ed. New York: W. H. Freeman; [2021]
[4] Lewin B. Genes X. 10th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning; [2011]
[5] Strachan T, Read A. Human Molecular Genetics. 5th ed. New York: Garland Science; [2019]
[6] Castillo Ruiz V, Dulijih Uranga Hernández R, Zafra de la Rosa G. Genética clínica. 2ª ed. México: Manual Moderno; s.f.
[7] Gafna. Estructura del gen. SlideServe. 2014 sep [17] Disponible en: https://www.slideserve.com/gafna/estructura-del-gen
[8] Mundogenetica. Estructura y partes de un gen. s.f. Disponible en: https://mundogenetica.jimdofree.com/tem%C3%A1ticas/1-bases-moleculares-de-la-herencia/1-2-estructura-y-partes-de-un-gen/
[9] Libretexts. (2021, 3 enero). [12]4: Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes. Biology LibreTexts. https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Cell_and_Molecular_Biology/Book%3A_Basic_Cell_and_Molecular_Biology_%28Bergtrom%29/12%3A_Regulation_of_Transcription_and_Epigenetic_Inheritance/12.04%3A_Gene_Regulation_in_Eukaryotes
[10] Bejerano G. Introduction to transcriptional regulation. Stanford University; s.f. Disponible en: https://bejerano.stanford.edu/readings/public/10_Intro_TxRegReview.pdf
[11] Libretexts. (2024d, noviembre 23). [16]7: Eukaryotic Gene Regulation - Transcriptional Enhancers and Repressors. Biology LibreTexts. https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_and_General_Biology/General_Biology_%28Boundless%29/16%3A_Gene_Expression/16.07%3A_Eukaryotic_Gene_Regulation_-_Transcriptional_Enhancers_and_Repressors
[12] Panigrahi A, O'Malley BW. Mechanisms of enhancer action: the known and the unknown. Genome Biol. 2021 Apr 15;22(1):108. doi: [10]1186/s13059-021-02322-1. PMID: 33858480; PMCID: PMC8051032.
[13] Akalin, A. (2020, 30 septiembre). [1]2 Elements of gene regulation | Computational Genomics with R. https://compgenomr.github.io/book/elements-of-gene-regulation.html
[14] Gordon F, Luger K, Hansen JC. The core histone N-terminal tail domains function independently and additively during salt-dependent oligomerization of nucleosomal arrays. J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 7;280(40):33701-6. doi: [10]1074/jbc.M507048200. Epub 2005 Jul [19] PMID: [16033758]
[15] Luger, K., & Hansen, J. C. (2005). The nucleosome. Nature, 437(7062), 1085-1086. https://doi.org/10.1038/4371085a
[16] Handel, A. E., & Ramagopalan, S. V. (2010). The genetics of epigenetics: what can we learn from twins? Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 103(1), 1-2.
[17] Esteller, M. (2008). Epigenetics in cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 358(11), 1148-1159. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra072067
[18] Weinberg, J., Szyf, M., & Meaney, M. J. (2006). Stress, DNA methylation and brain development. Developmental Psychobiology, 48(4), 271-290. https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.20147
[19] Allis, C. D., Jenuwein, T., Reinberg, D., & Caparros, M. L. (Eds.). (2007). Epigenetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
[20] Moore, L. D., Le, T., & Fan, G. (2013). DNA methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology, 38(1), 23-38. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.115
[21] Allis, C. D., Jenuwein, T., Reinberg, D., & Caparros, M. L. (Eds.). (2007). Epigenetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
[22] MedlinePlus. La nueva generación de vacunas de ARN mensajero frente a la gripe. Bethesda: U.S. National Library of Medicine; [2021] Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8397276/
[23] Smith, R.A., Andrews, K.S., Brooks, D., Fedewa, S.A., Manassaram-Baptiste, D., Saslow, D. and Wender, R.C. (2019), Cancer screening in the United States, 2019: A review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. CA A Cancer J Clin, 69: 184-210. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21557
[24] Wang T, Wei JJ, Sabatini DM, Lander ES. Genetic screens in human cells using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Science. 2014 Jan 3;343(6166):80-4. doi: [10]1126/science.1246981. Epub 2013 Dec [12] PMID: 24336569; PMCID: PMC3972032.
[25] Genotipia. Medicina genómica y farmacogenética. Genotipia; [2021] Disponible en: https://www.genotipia.com/medicina-genomica-y-farmacogenetica/
[26] Su J, Yang L, Sun Z, Zhan X. Personalized Drug Therapy: Innovative Concept Guided With Proteoformics. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2024 Mar;23(3):100737. doi: [10]1016/j.mcpro.2024.100737. Epub 2024 Feb [13] PMID: 38354979; PMCID: PMC10950891.
[27] García-Campelo, R., Sullivan, I., Arriola, E. et al. SEOM-GECP Clinical guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) (2022). Clin Transl Oncol 25, 2679–2691 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-023-03216-3
[28] Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(1):57-63. doi:10.1038/nrg2484
[29] Mortimer SA, Kidwell MA, Doudna JA. Insights into RNA structure and function from genome-wide studies. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(7):469-79. doi:10.1038/nrg3681
suscripcion
issnes
eISSN L 3072-9610 (English)
Information
Use of data and Privacy - Digital Adversiting
Infomedic International 2006-2025.

