Estructura de un gen y sus elementos de control
Autores/as
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37980/im.journal.ggcl.en.20252684Palabras clave:
genes, aplicaciones clínicas, revisión de la literaturaResumen
El conocimiento de la estructura, regulación y función de los genes es un pilar fundamental de la biología molecular y la medicina moderna. Los genes son secuencias de ADN que contienen la información necesaria para producir proteínas o ARN funcionales, y no solo están formados por regiones codificantes (exones), sino también por intrones y elementos reguladores como promotores, enhancers y silencers. Mutaciones en cualquiera de estas regiones pueden alterar la función celular normal y dar lugar a diversas enfermedades. La regulación de la expresión génica asegura que no todos los genes se activen al mismo tiempo, sino que lo hagan de manera controlada según el tipo celular, el momento del desarrollo o las condiciones ambientales. Este control está mediado por factores de transcripción, modificaciones epigenéticas como la metilación del ADN y la acción de ARN no codificantes, mecanismos que permiten que a partir de una misma secuencia de ADN se generen múltiples tipos celulares especializados. La función de los genes se refleja en los productos que codifican, ya sea proteínas o ARN, que participan en procesos vitales como el metabolismo, la señalización celular o la reparación del ADN. Las variantes genéticas pueden provocar pérdida de función, como en el caso de la fibrosis quística por mutaciones en el gen CFTR, o ganancia de función, como sucede en ciertos oncogenes implicados en cáncer.
INTRODUCCIÓN
Un gen es la unidad fundamental de la herencia y constituye un segmento definido de ADN que contiene la información necesaria para la síntesis de productos funcionales, ya sean proteínas o moléculas de ARN no codificante [1]. Estos elementos desempeñan un papel esencial en la transmisión de características hereditarias, en la regulación de procesos biológicos y en la diferenciación celular, lo que los convierte en piezas clave tanto para la biología molecular como para la medicina moderna [2].
La estructura de un gen no se limita a las secuencias que codifican proteínas (exones), sino que incluye múltiples regiones reguladoras que determinan cuándo, dónde y en qué cantidad se expresará un gen. Entre estas se encuentran el promotor, que permite el inicio de la transcripción; los intrones, secuencias no codificantes eliminadas en el proceso de maduración del ARN; y las regiones no traducidas (UTR), que regulan la estabilidad y traducción del ARNm [3]. Asimismo, los elementos de control proximales y distales, como las cajas TATA, CAAT, los potenciadores y silenciadores, modulan de manera precisa la actividad génica [1,4].
En conjunto, esta organización estructural y regulatoria asegura la correcta expresión de los genes, permitiendo que las células respondan a estímulos internos y externos, mantengan su identidad y coordinen funciones esenciales para el desarrollo y la homeostasis de los organismos vivos [5].
METODOLOGÍA
La presente investigación se llevó a cabo mediante una revisión bibliográfica. Para ello, se consultaron diferentes compendios de genética, incluyendo libros tanto en formato físico como digital. Asimismo, se revisaron artículos científicos actualizados, seleccionando aquellos que aportaran información relevante y fundamentada para el desarrollo del informe. Se procedió a extraer, analizar y sintetizar los datos más pertinentes, con el fin de construir un contenido claro y coherente orientado a la preparación de un material didáctico, dirigido a estudiantes de medicina y ciencias básicas.
¿Qué es un gen?
Un gen es la unidad física y funcional que ocupa una posición específica (locus) en el genoma. Corresponde a una secuencia de nucleótidos que codifica para uno o varios productos funcionales (ncRNA y polipéptidos) y cuya expresión está controlada por elementos reguladores [6].
Partes estructurales del gen (eucariotas)
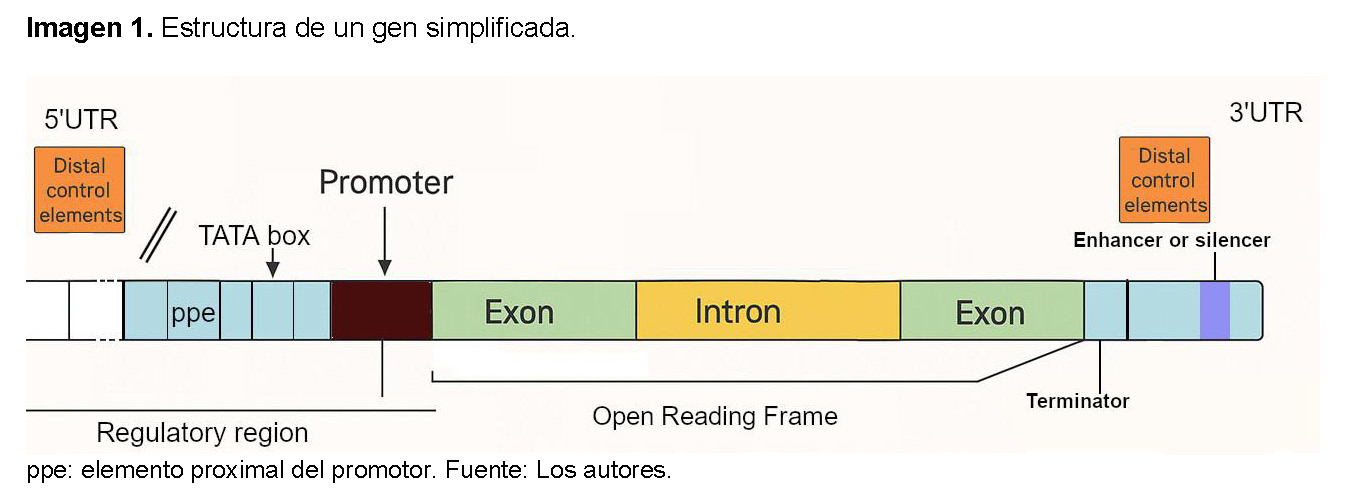
Los genes eucariotas presentan diversas regiones estructurales que controlan su expresión (Ver Imagen 1):
- Promotor: Es la región del ADN donde se une la ARN polimerasa y otros factores de transcripción para iniciar el proceso de transcripción.
- Exones: Son las secuencias de ADN que codifican la información para la síntesis de proteínas. Después de la transcripción, los exones se "empalman" (unen) para formar el ARNm maduro.
- Intrones: Son las secuencias de ADN no codificantes que se encuentran intercaladas entre los exones. Son transcritos a ARNm, pero luego son eliminados del ARNm inmaduro (pre-ARNm) mediante "splicing" (empalme) antes de que la proteína se sintetice. No se traducen a aminoácidos.
- Sitio de Inicio de la Transcripción (TSS): Es la primera base de ADN que es transcrita a ARN. Se encuentra dentro o justo después de la región promotora.
- Sitio de Inicio de la Traducción (Codón de Inicio): Es la secuencia de tres bases (generalmente AUG) en el ARNm que señala el comienzo de la síntesis de la proteína. Corresponde a un triplete específico en el ADN.
- Sitio de Terminación de la Traducción (Codón de Parada): Es la secuencia de tres bases que señala el final de la síntesis de la proteína.
- Regiones (Untranslated Regions): Son secuencias de ARN que están presentes en el ARNm maduro, pero no se traducen a proteína. 5' UTR: Se encuentra al inicio del ARNm, antes del codón de inicio. Influye en la estabilidad del ARNm y en la eficiencia de la traducción. 3' UTR: Se encuentra al final del ARNm, después del codón de parada.
- Secuencia Terminadora: Es una secuencia en el ADN que señala el final del proceso de transcripción. En eucariotas, a menudo incluye una secuencia que, en el ARNm, indica el sitio donde se añade una cola de poli-A (muchas adeninas) en el extremo 3' [7,8].
ELEMENTOS DE CONTROL GÉNICO
Elementos de control proximales
Los elementos de control proximales son secuencias de ADN reguladoras que se encuentran cerca del inicio de la transcripción de un gen. Su propósito principal es controlar la transcripción, es decir, el proceso de "leer" la información del gen para crear proteínas. Estos elementos se localizan en una región cercana al sitio de inicio de la transcripción, generalmente dentro de unos pocos cientos de pares de bases río arriba, y funcionan como puntos de anclaje para proteínas especializadas que modulan la expresión génica [9].
Dentro de esta región, existen dos tipos de elementos cruciales. El primero es el promotor basal, que es la secuencia de ADN más cercana al sitio de inicio de la transcripción y es indispensable para que el proceso ocurra. Es aquí donde la enzima ARN polimerasa se une junto con los factores de transcripción generales para formar el complejo de preiniciación. Un ejemplo clave dentro del promotor basal es la Caja TATA, una secuencia que ayuda a posicionar la maquinaria de transcripción de forma correcta. El segundo tipo son los elementos reguladores proximales, que se ubican justo antes del promotor basal. Estas secuencias son reconocidas por factores de transcripción específicos que actúan como interruptores, aumentando (activadores) o disminuyendo (represores) la actividad del promotor basal para afinar la tasa de transcripción. Ejemplos de estos elementos incluyen la Caja CAAT y la Caja GC [9].
En esencia, los elementos de control proximales funcionan como plataformas de unión. Al modular la tasa de transcripción, estos elementos son fundamentales para la especificidad de la expresión génica. Esto asegura que los genes se activen o desactiven en el momento y lugar adecuados, permitiendo que una célula se especialice y responda a las señales [9].
Elementos de control distales
Los elementos de control distal de un gen son secuencias de ADN reguladoras que se encuentran lejos del sitio de inicio de la transcripción del gen al que afectan, a diferencia de los elementos proximales que están cerca [10,11].
Los dos tipos son:
- Potenciadores (enhancers): son secuencias de ADN que aumentan la tasa de transcripción de un gen y actúan uniendo factores de transcripción. Estos factores, a su vez, interactúan con el complejo de transcripción basal en el promotor del gen, a menudo a través del plegamiento del ADN, formando bucles para acercar las regiones distales a las proximales. La acción de los potenciadores es a menudo específica de tejido o etapa de desarrollo, lo que permite una regulación fina de la expresión génica en diferentes contextos celulares [11,12].
- Silenciadores (silencers): son secuencias de ADN que, por el contrario, disminuyen o suprimen la tasa de transcripción de un gen También pueden encontrarse a distancias considerables del gen diana.Al igual que los potenciadores, los silenciadores actúan uniéndose a factores de transcripción represores de varias maneras como: bloqueando la unión de factores de transcripción activadores, reclutando proteínas que modifican la cromatina para hacerla más compacta, o interfiriendo directamente con la maquinaria de transcripción [11,13].
Regulación Epigenética Y Cromatina
La Cromatina y su Función
La cromatina es la estructura compuesta por ADN y proteínas que empaqueta el material genético en el núcleo celular. Su principal función es compactar el ADN para que pueda caber en el espacio reducido del núcleo [1]. Esta estructura no es fija, sino que puede alternar entre un estado condensado (heterocromatina) y uno más relajado (eucromatina). Esta maleabilidad es crucial para la regulación génica, ya que los genes sólo pueden ser leídos por la maquinaria celular cuando la cromatina se encuentra en su estado más laxo [14,15].
Regulación Epigenética
La regulación epigenética se refiere a las modificaciones que afectan la expresión de los genes sin alterar la secuencia del ADN. El término "epi" (que significa "sobre") resalta que estos mecanismos actúan por encima del código genético [16]. Estos cambios son esenciales para la diferenciación celular, son influenciados por factores ambientales como el estrés o la dieta, y, a diferencia de las mutaciones, son reversibles y pueden ser heredados por las células hijas y, en algunos casos, por la descendencia [17,18].
Mecanismos epigenéticos
Los principales mecanismos epigenéticos funcionan a través de la modificación de la cromatina [19]. La metilación del ADN, que consiste en agregar grupos metilo a las bases de citosina, suele silenciar los genes al impedir la transcripción (Ver Figura 2) [20]. De manera similar, las modificaciones de histonas, como la acetilación y la metilación, alteran la compactación de la cromatina. La acetilación, por ejemplo, tiende a relajar la estructura y facilitar la transcripción, mientras que la metilación puede tener efectos de activación o represión, dependiendo de la histona específica que se modifique [21].
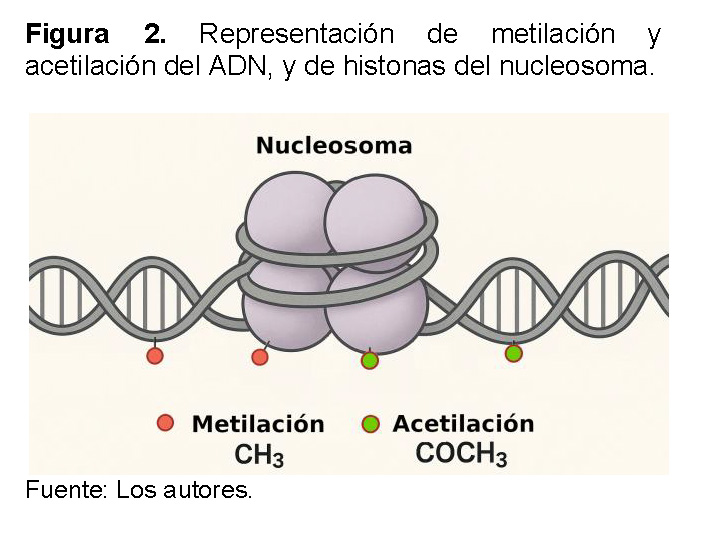
Los nucleosomas son una pieza clave en este proceso porque su estructura y las modificaciones químicas que experimentan determinan el grado de compactación de la cromatina, que es el material del que están hechos los cromosomas. Cuando la cromatina está muy compactada, se llama heterocromatina y el ADN es inaccesible, lo que silencia los genes. Por el contrario, cuando la cromatina está relajada, conocida como eucromatina, el ADN queda expuesto y los genes pueden ser transcritos y expresados.

CONCLUSIÓN
Un gen es una unidad funcional del ADN que ocupa un locus específico y posee estructuras como promotores, exones, intrones y regiones UTR que determinan su expresión. Estos genes están regulados por elementos de control proximales (como la caja TATA) y distales (como potenciadores y silenciadores), que permiten ajustar su actividad de manera precisa. Además, la cromatina, en forma de heterocromatina o eucromatina, regula el acceso al ADN y está influenciada por mecanismos epigenéticos como la metilación y acetilación de histonas. Estas regulaciones son esenciales para el desarrollo, la diferenciación celular y la respuesta a estímulos ambientales. En medicina, el estudio de los genes permite diagnosticar enfermedades, diseñar tratamientos personalizados, aplicar terapias génicas y monitorear la progresión de patologías.
Agradecimientos
Agradecemos al Dr. Jorge Mendez Rios, por su apoyo en la redacción y revisión crítica de este manuscrito.
Referencias
[1] Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Morgan D, Raff M, Roberts K, et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 6th ed. New York: Garland Science; [2014]
[2] Watson JD, Baker TA, Bell SP, Gann A, Levine M, Losick R. Molecular Biology of the Gene. 7th ed. San Francisco: Pearson; [2013]
[3] Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky SL, Matsudaira P, Baltimore D, Darnell J. Molecular Cell Biology. 9th ed. New York: W. H. Freeman; [2021]
[4] Lewin B. Genes X. 10th ed. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning; [2011]
[5] Strachan T, Read A. Human Molecular Genetics. 5th ed. New York: Garland Science; [2019]
[6] Castillo Ruiz V, Dulijih Uranga Hernández R, Zafra de la Rosa G. Genética clínica. 2ª ed. México: Manual Moderno; s.f.
[7] Gafna. Estructura del gen. SlideServe. 2014 sep [17] Disponible en: https://www.slideserve.com/gafna/estructura-del-gen
[8] Mundogenetica. Estructura y partes de un gen. s.f. Disponible en: https://mundogenetica.jimdofree.com/tem%C3%A1ticas/1-bases-moleculares-de-la-herencia/1-2-estructura-y-partes-de-un-gen/
[9] Libretexts. (2021, 3 enero). [12]4: Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes. Biology LibreTexts. https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Cell_and_Molecular_Biology/Book%3A_Basic_Cell_and_Molecular_Biology_%28Bergtrom%29/12%3A_Regulation_of_Transcription_and_Epigenetic_Inheritance/12.04%3A_Gene_Regulation_in_Eukaryotes
[10] Bejerano G. Introduction to transcriptional regulation. Stanford University; s.f. Disponible en: https://bejerano.stanford.edu/readings/public/10_Intro_TxRegReview.pdf
[11] Libretexts. (2024d, noviembre 23). [16]7: Eukaryotic Gene Regulation - Transcriptional Enhancers and Repressors. Biology LibreTexts. https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_and_General_Biology/General_Biology_%28Boundless%29/16%3A_Gene_Expression/16.07%3A_Eukaryotic_Gene_Regulation_-_Transcriptional_Enhancers_and_Repressors
[12] Panigrahi A, O'Malley BW. Mechanisms of enhancer action: the known and the unknown. Genome Biol. 2021 Apr 15;22(1):108. doi: [10]1186/s13059-021-02322-1. PMID: 33858480; PMCID: PMC8051032.
[13] Akalin, A. (2020, 30 septiembre). [1]2 Elements of gene regulation | Computational Genomics with R. https://compgenomr.github.io/book/elements-of-gene-regulation.html
[14] Gordon F, Luger K, Hansen JC. The core histone N-terminal tail domains function independently and additively during salt-dependent oligomerization of nucleosomal arrays. J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 7;280(40):33701-6. doi: [10]1074/jbc.M507048200. Epub 2005 Jul [19] PMID: [16033758]
[15] Luger, K., & Hansen, J. C. (2005). The nucleosome. Nature, 437(7062), 1085-1086. https://doi.org/10.1038/4371085a
[16] Handel, A. E., & Ramagopalan, S. V. (2010). The genetics of epigenetics: what can we learn from twins? Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 103(1), 1-2.
[17] Esteller, M. (2008). Epigenetics in cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 358(11), 1148-1159. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra072067
[18] Weinberg, J., Szyf, M., & Meaney, M. J. (2006). Stress, DNA methylation and brain development. Developmental Psychobiology, 48(4), 271-290. https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.20147
[19] Allis, C. D., Jenuwein, T., Reinberg, D., & Caparros, M. L. (Eds.). (2007). Epigenetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
[20] Moore, L. D., Le, T., & Fan, G. (2013). DNA methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology, 38(1), 23-38. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.115
[21] Allis, C. D., Jenuwein, T., Reinberg, D., & Caparros, M. L. (Eds.). (2007). Epigenetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
[22] MedlinePlus. La nueva generación de vacunas de ARN mensajero frente a la gripe. Bethesda: U.S. National Library of Medicine; [2021] Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8397276/
[23] Smith, R.A., Andrews, K.S., Brooks, D., Fedewa, S.A., Manassaram-Baptiste, D., Saslow, D. and Wender, R.C. (2019), Cancer screening in the United States, 2019: A review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. CA A Cancer J Clin, 69: 184-210. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21557
[24] Wang T, Wei JJ, Sabatini DM, Lander ES. Genetic screens in human cells using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Science. 2014 Jan 3;343(6166):80-4. doi: [10]1126/science.1246981. Epub 2013 Dec [12] PMID: 24336569; PMCID: PMC3972032.
[25] Genotipia. Medicina genómica y farmacogenética. Genotipia; [2021] Disponible en: https://www.genotipia.com/medicina-genomica-y-farmacogenetica/
[26] Su J, Yang L, Sun Z, Zhan X. Personalized Drug Therapy: Innovative Concept Guided With Proteoformics. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2024 Mar;23(3):100737. doi: [10]1016/j.mcpro.2024.100737. Epub 2024 Feb [13] PMID: 38354979; PMCID: PMC10950891.
[27] García-Campelo, R., Sullivan, I., Arriola, E. et al. SEOM-GECP Clinical guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) (2022). Clin Transl Oncol 25, 2679–2691 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-023-03216-3
[28] Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(1):57-63. doi:10.1038/nrg2484
[29] Mortimer SA, Kidwell MA, Doudna JA. Insights into RNA structure and function from genome-wide studies. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(7):469-79. doi:10.1038/nrg3681
suscripcion
issnes
eISSN 2953-3139 (Spanish)

